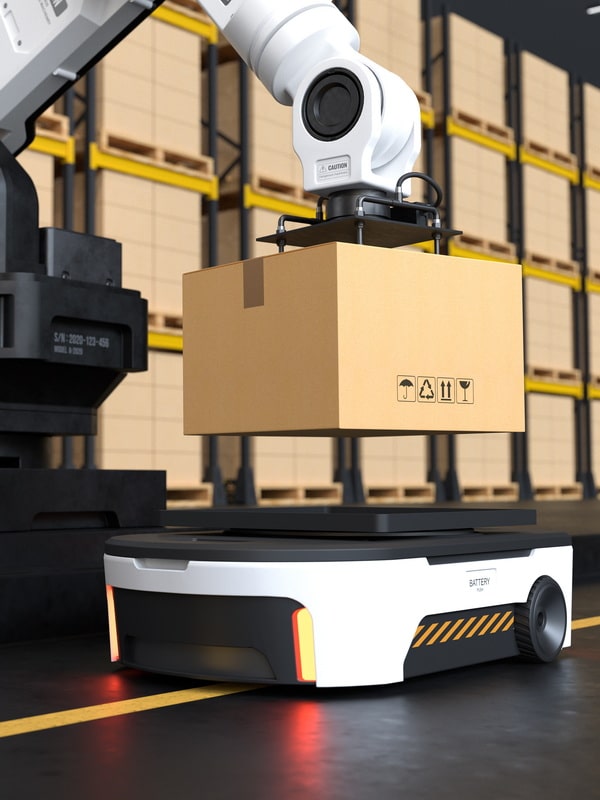
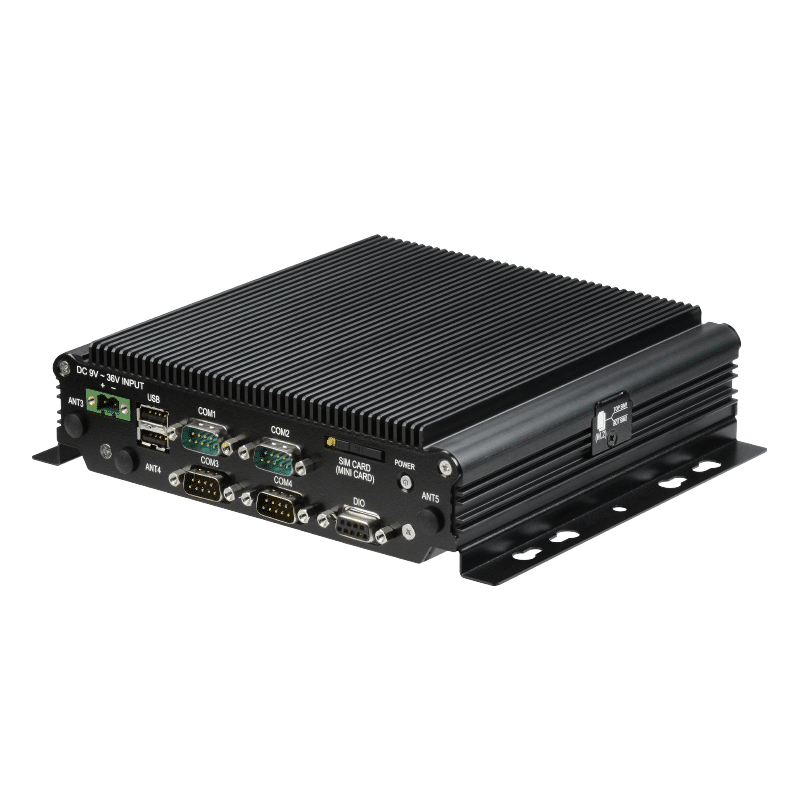
SINTRONES demonstrates exceptional technical prowess and commercial advantages in applying Autonomous Mobile Robots (AMR) and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGV). The ABOX-5211 series industrial computer, launched by SINTRONES, is specially designed for these sophisticated robot systems and possesses several superior features.
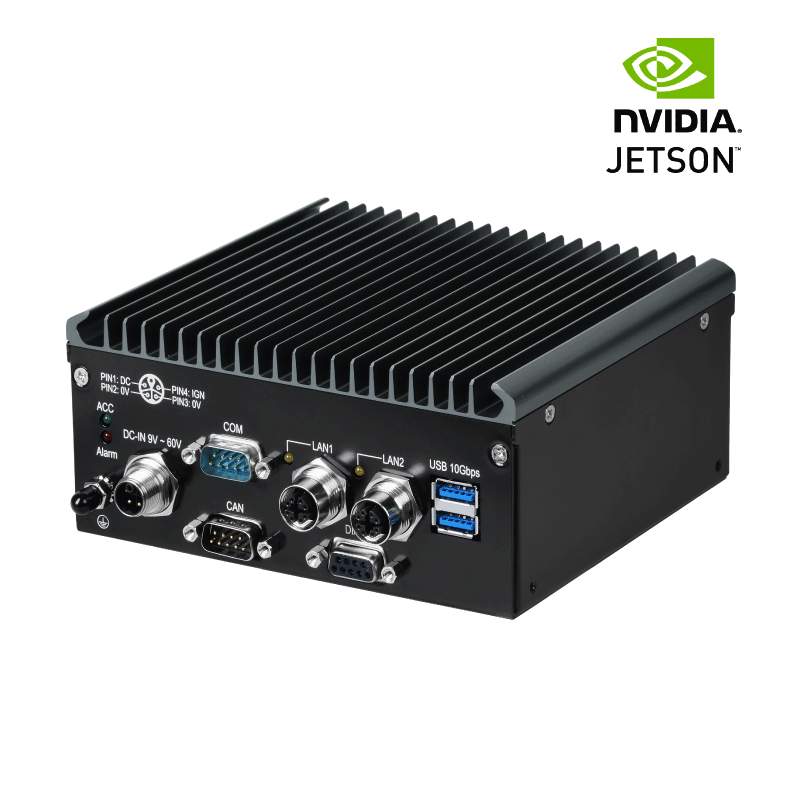
Firstly, the ABOX-5211 series industrial computer is equipped with a powerful 10th-generation Intel Core i9 processor, ensuring it can operate at peak performance to handle various highly complex automation tasks. This robust processing power gives SINTRONES products a competitive edge in the market.
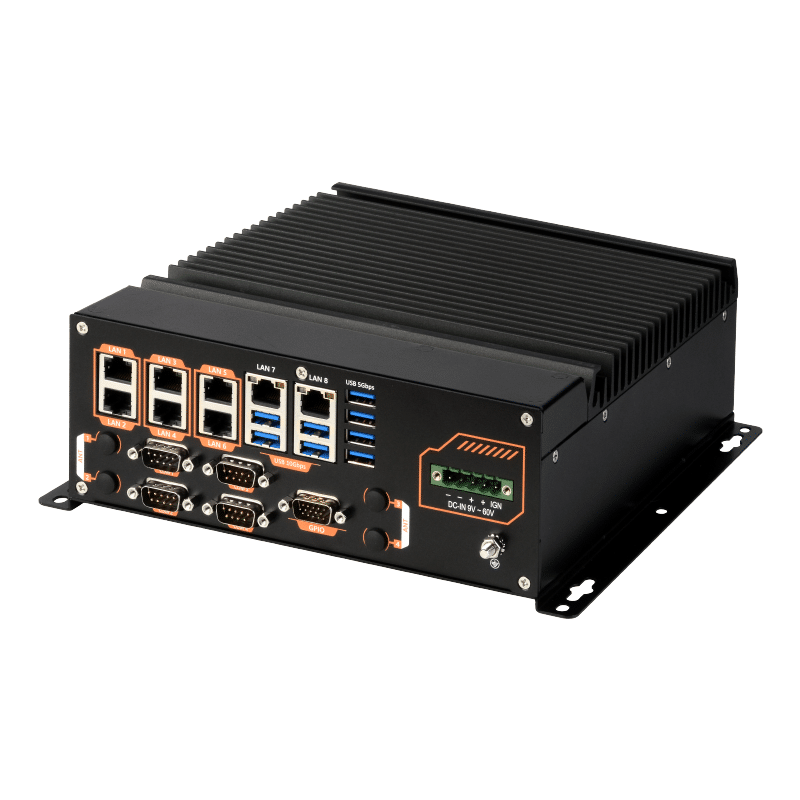
Secondly, the ABOX-5211 has 8 GbE ports. It can optionally be equipped with 8 Power-over-Ethernet (PoE) ports, allowing this industrial computer to establish quick and stable connections with other devices and systems, thereby enhancing overall operational efficiency.
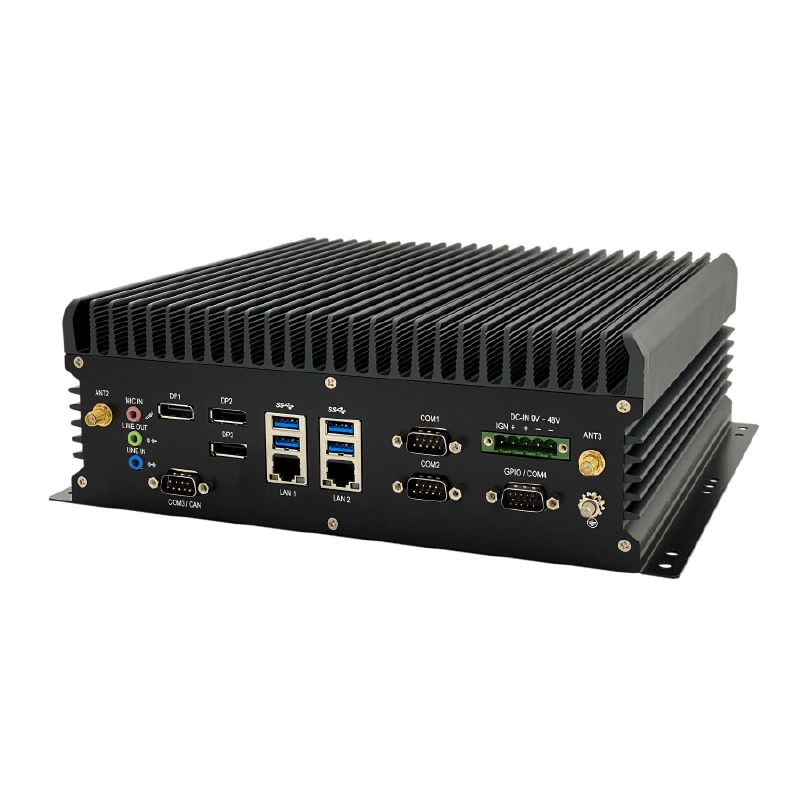
In addition, the ABOX-5211 also supports 5G, LTE, and Wi-Fi communication modules, enabling AMRs and AGVs to achieve fast and stable data transmission in wireless network environments, allowing robots to complete tasks more quickly and accurately.
In terms of design, the ABOX-5211 adopts a “One-sided I/O Focusing” integrated design, placing all vital external device connection interfaces on the same side. This feature facilitates user expansion and maintenance of the equipment, further enhancing user experience. Furthermore, SINTRONES has over a decade of R&D experience and earned a good reputation in the global market. This enables them to better understand customer needs and provide adaptive solutions for market changes. SINTRONES has evident advantages in the relevant applications of AMR and AGV. Their strong technical capabilities, innovative design philosophy, and profound R&D experience place them in a leading position in this field.